NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0: An Overview

Table of contents
On February 26, 2024, the new NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 was released by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in collaboration with stakeholders from organizations of all sizes.
The NIST framework guides organizations to manage cybersecurity risks with its taxonomy of high-level cybersecurity outcomes that can be used by any organization—regardless of its size, sector, or maturity. The framework helps organizations to better understand, assess, prioritize, and communicate their cybersecurity efforts for a better cybersecurity posture.
What Is NIST CSF 2.0?
The scope of NIST CSF 2.0 has also been expanded to address global cybersecurity challenges, moving beyond its initial focus on U.S. critical infrastructure. Now, all organizations can make use of NIST practices, regardless of sector.
The cyber framework includes the following components:
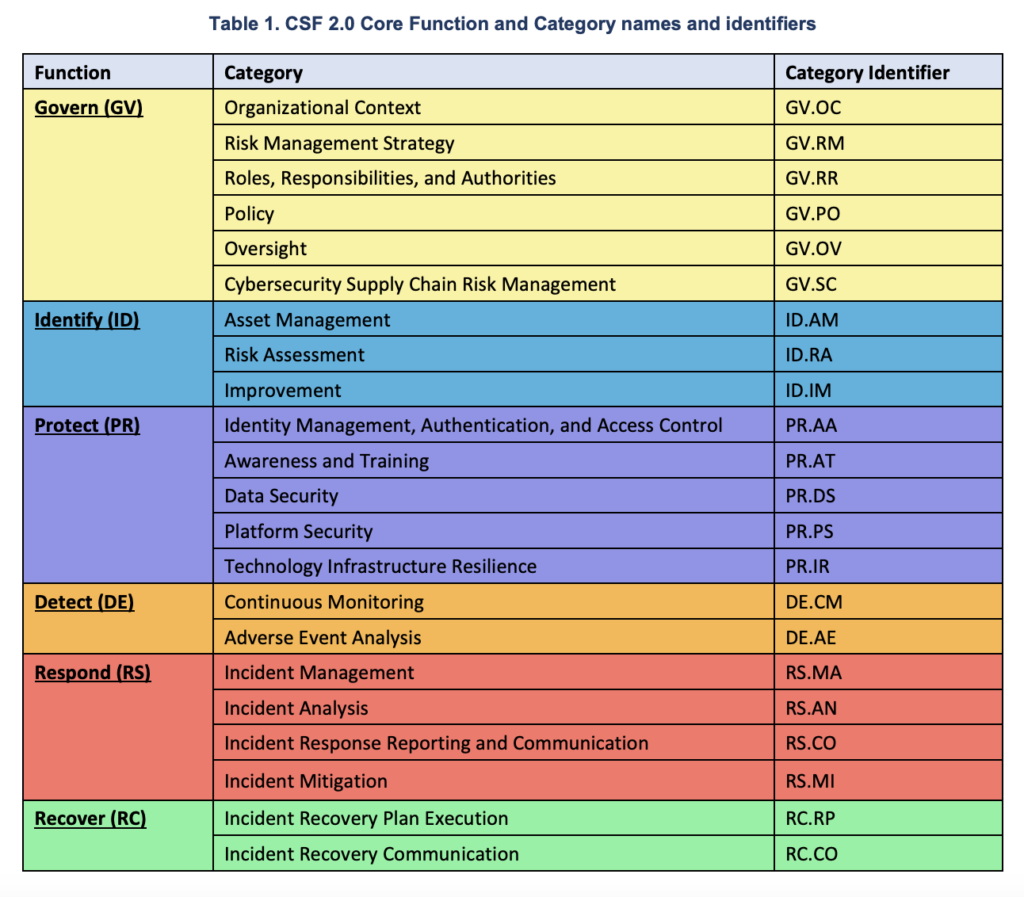
- CSF Core. The taxonomy of high-level cybersecurity outcomes that helps organizations manage their cybersecurity risks. The CSF Core components are a hierarchy of functions, categories, and subcategories that detail each outcome applying to all information technology (IT) systems.
- CSF Organizational Profiles. Details the mechanics for describing an organization‘s target cybersecurity posture.
- CSF Tiers. Tiers provide context for how an organization views its cybersecurity risks, and the. processes to manage those risks including governance and management practices.
Why is the NIST Framework essential for cybersecurity compliance?
NIST CSF 2.0 is widely recognized as a critical resource for organizations seeking to improve their cybersecurity posture.
Organizations can map various cybersecurity standards with the NIST framework to adhere to regulatory requirements for identifying, detecting, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents.
NIST compliance provides a comprehensive foundation that aligns with many existing compliance standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO, and CIS Controls.
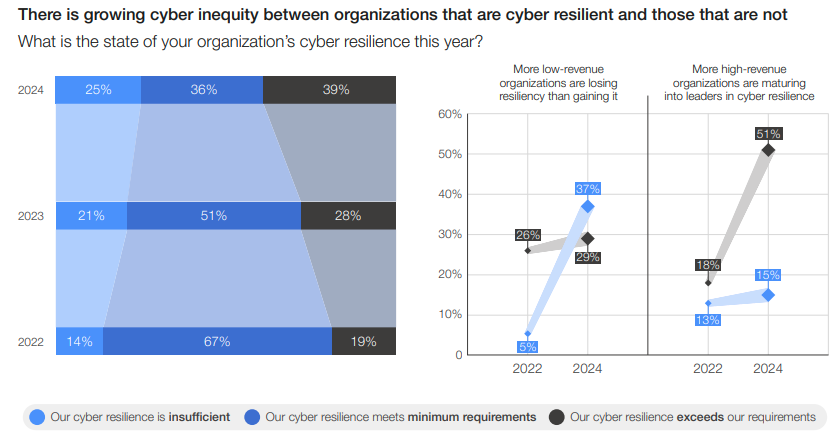
Governance is a new core function of NIST CSF 2.0
To develop the new NIST Cybersecurity Framework, NIST worked directly with stakeholders to address the most recent cybersecurity challenges.
One significant change to the framework is the addition of a new Govern function. The new key function helps organizations make informed decisions on policy and management practices aligned to a larger cybersecurity strategy, including organizational context, risk management strategies, and supply chain risk management.
NIST 2.0 can support European organizations to implement cybersecurity best practices
The European Union implemented the NIS 2 directive in October 2024 to establish a unified legal framework to uphold cybersecurity in 18 critical sectors across the EU. However, the directive isn‘t a framework in itself but rather, a set of requirements organizations must uphold.
The NIST CSF 2.0 framework can support EU nations and organizations to implement the NIS 2 directive. NIST has many implementation examples from various organizations sizes and sectors to support best cybersecurity practices.
What are the 5 pillars of NIST CSF 2.0?
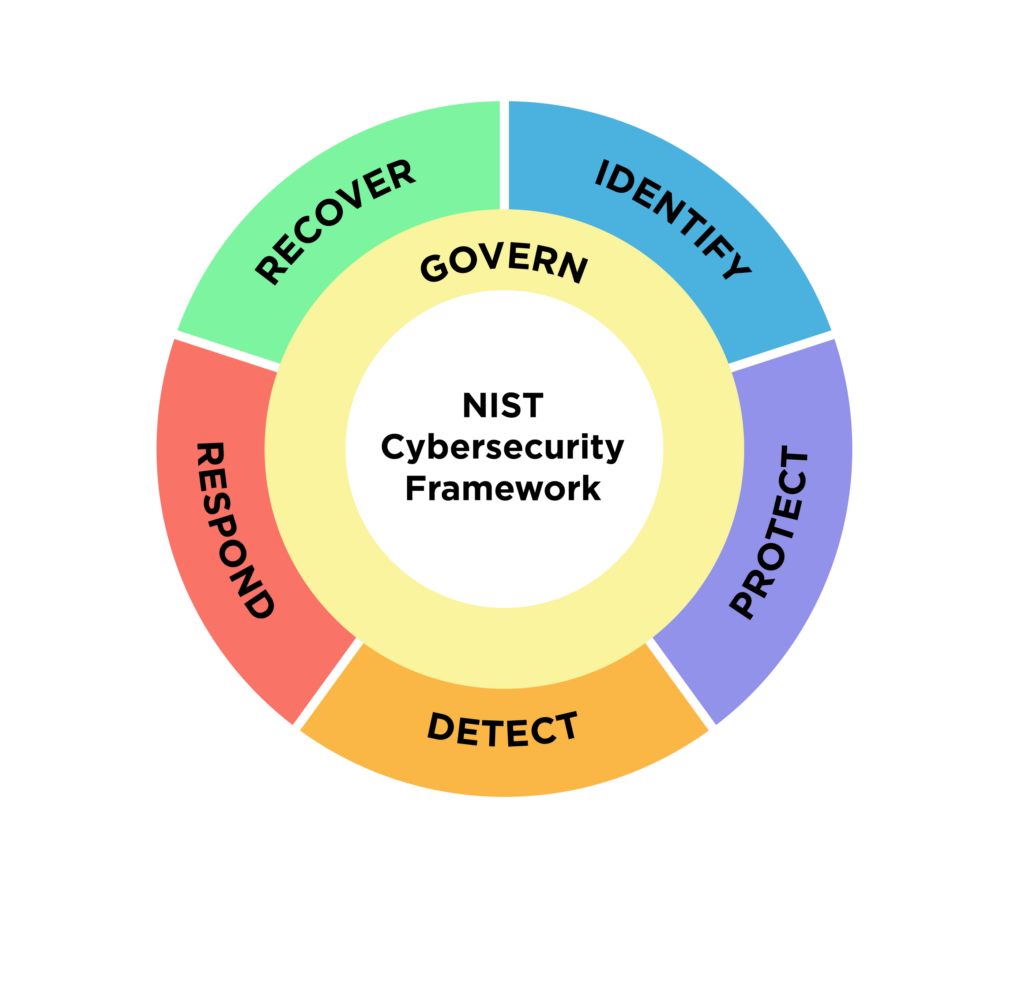
The NIST framework is organized into 5 core functions from version 1.1, plus the new Govern function added to version 2.0.
The core functions of NIST CSF 2.0 are:
- Govern—The Govern function provides outcomes for the organization‘s ability to achieve and prioritize the five other functions. To reduce cybersecurity risk, it‘s important to consider the broader organizational context for sustainable results, including establishing a cybersecurity strategy, considering cybersecurity supply chain risk management (including roles, responsibilities, and authorities), and cybersecurity compliance with regulatory bodies.
- Identify—The Identify function asks organizations to consider their current cybersecurity threat landscape, and identify areas for improvement within the policies, plans, processes, procedures, and management practices.
- Protect—The Protect function addresses safeguards to manage the organization‘s cyber risk, preventing vulnerabilities from being exploited. It‘s important to address areas such as identity management, access control, data security, platform security, and infrastructure resilience.
- Detect—The Detect function determines how quickly organizations can discover a potential threat and analyze adverse events that indicate cyberattacks. This function supports successful incident response and recovery activities for enhanced mitigation of threats.
- Respond—The Respond function provides guidelines for actions to take after a threat is uncovered to contain cyber threats. It covers incident management, analysis, mitigation, reporting, and communication of cyber attacks.
- Recover—The Recover function helps organizations identify assets and operations impacted by a cyber attack and supports the organization’s return to normal operation.
Key benefits of implementing NIST CSF 2.0
As new applications of technology emerge, such as AI, new privacy and cybersecurity risks emerge. The framework was developed to help address these risks.
Implementing NIST CSF 2.0 can help organizations to:
- Meet regulatory requirements: NIST CSF 2.0 is aligned with standards like ISO, HIPAA, and GDPR, helping businesses meet different compliance requirements.
- Improve supply chain transparency: Manage modern cyber risks, fostering trust between the business, customers, and service providers.
- Build a resilient cyber risk management strategy: NIST CSF 2.0 provides organizations with a jumping-off point when developing their cybersecurity risk management strategy. Use the guidelines to create TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, and Protocols) that align with the company‘s goals.
- Adaptive and flexible for all organizations: The adaptable structure of NIST CSF 2.0 means that any organization can implement the advice—from small businesses to enterprise scale.
- Future-proof your organization: Organizations and government bodies that use the NIST Framework are more resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats, encouraging sustainable growth.
A construction company lost $550,000 to a keylogging attack
Employees of a small construction company logged into company systems with their user-specific ID. Not long after, the owner was notified that in one week cybercriminals had made six transfers from company bank accounts totaling $550,000 to an unknown source.
It was revealed that cybercriminals had installed key-logging malware onto the company‘s systems to capture banking credentials. The bank was only able to retrieve $200,000 leading to a loss of $350,000. The construction company did not have any cybersecurity programs or plans in place to prevent an attack.
The NIST CSF 2.0 framework could have supported the company to implement:
- Notifications for transactions: Set up transaction alerts on all bank accounts to be notified when a transaction is being made.
- Restricted access: Ensure that sensitive accounts are only available to employees who need access for their role. Regularly changing passwords is important for reducing risk.
- Risk management policies: Evaluate cybersecurity risk such as with a risk assessment to determine risk tolerance.
- Incident response plan: Companies with an incident response plan have better cybersecurity outcomes.
- Employee training: Training staff to respond to incidents like phishing helps mitigate adverse cybersecurity events.
A hotel lost $1 million to a phishing threat
The CEO of a boutique hotel realized they were a victim of wire fraud when the hotel did not have the funds to pay ongoing expenses. A few weeks previous to the attack, the CEO had clicked on a malicious link in an email they believed was from the IRS.
Through a social-engineered phishing attack, the cybercriminals were able to capture the CEO‘s login credentials, giving them full access to the company‘s internal systems. The company lost $1 million to an account in China.
To prevent another attack, the company can use the NIST CSF 2.0 framework to:
- Train staff about phishing risks: Employees need to be aware of the dangers of clicking on malicious links and suspicious email attachments, how to identify fraudulent emails, and have regular security training.
- Implement stringent wire transfer protocols: This includes multi-factor authentication (MFA) and other secondary forms of validating transfers.
- Have a cyber incident response plan: Implementing an incident response plan ensures that even if an attack occurs, the company can respond without facing more potential losses.
How can organizations implement NIST CSF 2.0 in their cybersecurity strategy?
NIST CSF 2.0 can be implemented by any business size, from small business to enterprise with its extensive informative resources.
The Enterprise Risk Management Quick Start Guide is one free resource that helps organizations assess their risk tolerance by recording risks across the enterprise in a common register format.
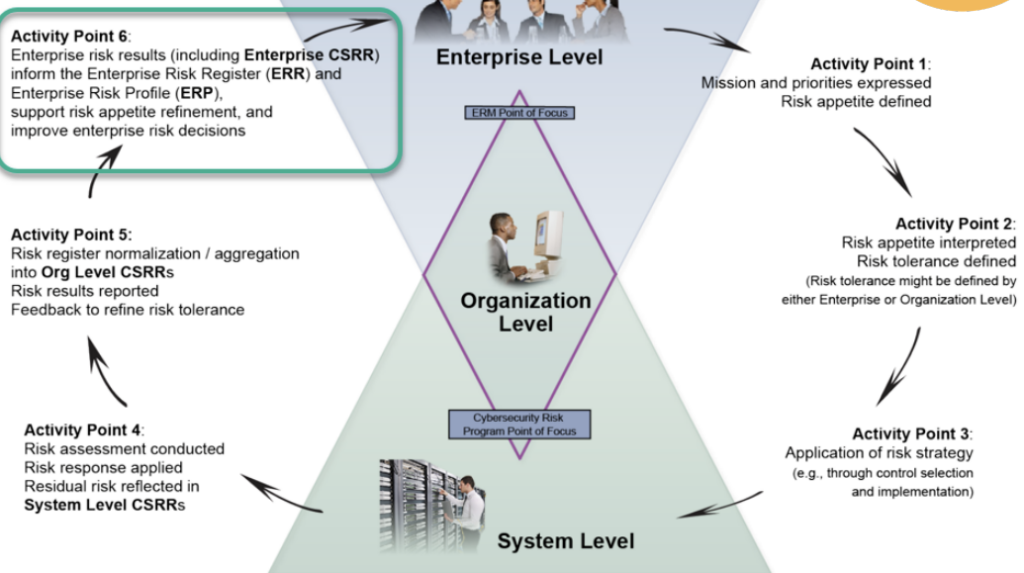
Here‘s how to get started implementing NIST CSF 2.0:
- Understand the framework: Dive into the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, including its five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Pay special attention to the new “Govern” function, which focuses on governance and risk management.
- Engage leadership and stakeholders: Gain commitment from organizational leadership and involve key stakeholders to ensure alignment with business goals and regulatory requirements.
- Assess current state: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of your organization’s current cybersecurity posture, identifying strengths, weaknesses, risks, and compliance gaps.
- Define a target state: Set clear objectives for the desired cybersecurity posture based on your organization’s risk tolerance, legal requirements, and business priorities.
- Develop a roadmap: Create an actionable plan to address gaps and achieve your target state. This should include prioritized initiatives, timelines, and resource allocation.
- Implement controls and processes: Establish or enhance security measures, policies, and procedures that align with NIST 2.0 guidelines.
- Monitor and measure progress: Use metrics to track progress, measure effectiveness, and ensure continuous improvement. Regularly revisit and refine your strategy to adapt to evolving threats and requirements.
- Conduct ongoing training and awareness: Educate employees about cybersecurity risks, and best practices to foster a culture of security.
How can small businesses implement NIST CSF 2.0?
Businesses that do not have an existing cybersecurity strategy can start to implement NIST CSF 2.0 with templates and information provided by NIST.
The Small Business Quick Start Guide makes suggestions for each of the 6 core functions to guide small businesses through the process of creating cybersecurity infrastructure.
FAQs
- What are the key differences between NIST CSF 1.1 and 2.0? The NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 builds upon the previous version 1.1 released in 2018. The updated NIST framework has a broader focus to apply across industries, including new framework guidelines for governance.
- How does NIST CSF 2.0 help organizations meet regulatory requirements? NIST CSF 2.0 helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by mapping cybersecurity practices to regulations, focusing on risk management, and promoting continuous improvement. The framework‘s adaptability and structured approach make it easier to align with diverse regulatory standards and ensure compliance.
- Can small businesses benefit from adopting NIST CSF 2.0? The NIST framework helps small businesses identify and mitigate risks, enhance trust with customers and partners, meet regulatory requirements efficiently, and build resilience against cyber threats—without requiring extensive resources.
- What resources are available to assist with implementation? NIST provides a searchable catalog of informative references that allows users to cross-reference the framework’s guidance to more than 50 other cybersecurity documents. The CSF 2.0 Reference Tool simplifies the way organizations can implement the framework, allowing users to browse, search, and export data and details from the CSF’s core guidance in human-consumable and machine-readable formats.
- How does the “Govern” function improve compliance efforts? The additional Govern function in NIST CSF 2.0 strengthens compliance efforts by establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing cybersecurity risks. By implementing governance strategies, organizations can better align with regulatory requirements and have oversight of cybersecurity practices.
- What role does real-time threat intelligence play in achieving compliance? The NIST CSF 2.0 framework enables organizations to proactively address cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities by providing up-to-date insights. Creating a strategy for monitoring and responding to risks in real-time ensures sensitive data is protected and compliance is upheld.
Manage your cybersecurity risks with NIST CSF 2.0
To protect critical infrastructure as cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must take an adaptive approach to their cybersecurity posture.
NIST CSF 2.0 represents a vital advancement in cybersecurity practices with a flexible and proactive approach to managing risks and ensuring compliance. The added Govern function empowers entities of all sizes to strengthen their cybersecurity posture and protect critical assets.
Ensure cybersecurity compliance with CybelAngel’s solutions
CybelAngel‘s comprehensive EASM platform can monitor and detect threats across your IT infrastructure in real-time.
See how you can use CybelAngel in conjunction with the NIST CSF 2.0 framework for unparalleled coverage.

