Navigating US-China Cyber Conflicts

Table of contents
The relationship between the U.S. government and China has always been contentious, characterized by strategic mistrust, confrontation, and conflict.
Tension between the two sides has only grown in the last five years. Specialists have stated that the US- China relationship has passed a tipping point, leading to further uncertainty worldwide.

So how will Chinese cyber espionage impact US security and the rest of the world?
Let‘s dive into how Chinese state-sponsored hacking is being used to undermine cybersecurity.
Are hackers the biggest threat to America’s critical infrastructure?
U.S. intelligence agencies have identified the PRC as the top military and cyber threat, with Chinese nationals acting as employees of private companies deploying operations like Volt Typhoon, Salt Typhoon, and iSoon.
What was the aim of the PRC in performing these attacks? According to the Justice Department, the threat actors sought to extract profit and identify information that could be sold directly or indirectly to the PRC government.
The Justice Department and FBI announced that they will continue to crack down on dissident activities and hacking groups from the People‘s Republic of China to protect Americans and US national security.
FBI Director Christopher Wray warned national security and intelligence experts during the Vanderbilt Summit of the risks the government of China poses to the U.S.
“The PRC’s targeting of our critical infrastructure is both broad and unrelenting…driven by the CCP’s aspirations to wealth and power.”
Timeline of attacks
In the last years, Beijing has engaged in cyber espionage targeting the US, Europe, and Indonesia, hacking technology companies and disrupting critical infrastructure to destabilize the West.
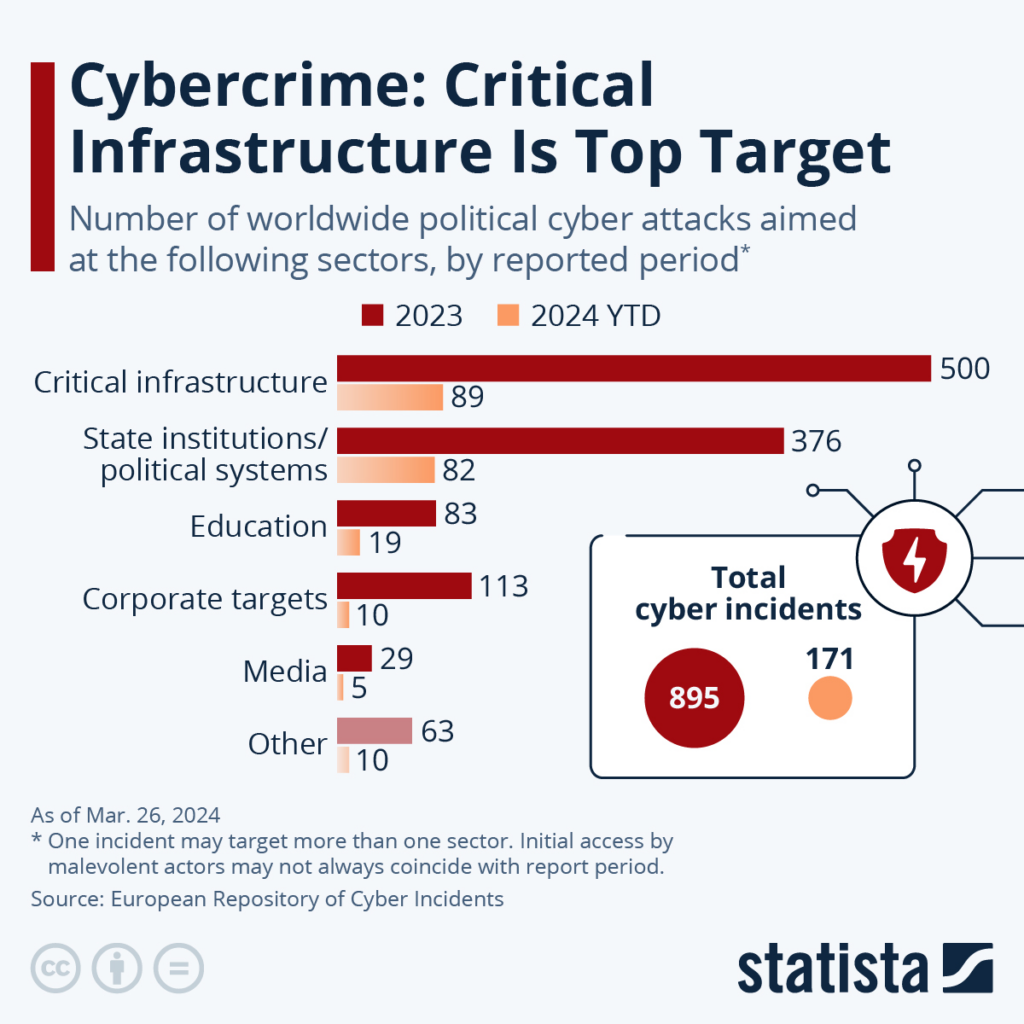
Here‘s a quick timeline of notable attacks made by China in recent years:
- February 2022, Ukraine war tactics
China conducted phishing campaigns against the European Union with malware embedded into fake Ukraine-related reports. - May 2023, US authorities exposed Volt Typhoon
Law enforcement uncovered information about activity attributed to Volt Typhoon. - February 2024, iSoon activities are leaked to GitHub
The activities of Chinese hacker group iSoon were leaked to GitHub. The documents exposed how hackers were colluding with the PRC as part of their cyber espionage efforts. - October 2024, Intrusions into Trump‘s cellphone
Chinese hackers compromised cellphones used by members of the Trump administration, including phones used by presidential candidate Donald Trump, JD Vance, and other officials associated with the Harris-Walz campaign. - November 2024, Salt Typhoon breached US telecom providers
Chinese hacker group Salt Typhoon breached at least 8 US telecom providers. The threat actors stole law enforcement surveillance data to compromise U.S. officials and individuals involved with the White House. - November 2024, Chinese spies tracked a US general
Chinese spies planted a chip in a former U.S. general’s conference name tag to track his movements during his time served in the Indo-Pacific region. - December 2024, US Treasury hacked by Beijing
Chinese state-sponsored hackers breached the US Treasury Department and stole over 3,000 unclassified documents. The documents were related to prominent US lawmakers. - March 2025, US indicts 10 Chinese hackers
The White House indicts 10 alleged Chinese hackers for iSoon hacking activities.
Volt Typhoon malware targets US critical infrastructure
In 2024, Volt Typhoon, a China-based state-sponsored group, targeted the “Five Eyes” coalition with cyberattacks.
According to Aljazeera, Microsoft researchers said Volt Typhoon was developing capabilities “that could disrupt critical communications infrastructure between the United States and Asia region during future crises.”
Active since 2021, the hackers focused their attacks on U.S. critical infrastructure and exploited vulnerabilities such as weak administrator passwords using living-off-the-land techniques.
Volt Typhoon’s existence and the escalating tensions between China and the U.S., particularly over Taiwan, underscore the latest connection between global events and cybersecurity.
Cyber espionage from hacking operation Salt Typhoon
Salt Typhoon, a Chinese APT group linked to China’s Ministry of State Security, has conducted cyber espionage since 2019, targeting sectors like telecommunications and government entities globally.
In 2024, the Biden administration exposed the group‘s operations in Europe and Asia, prompting the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to release guidelines for protecting critical service providers.
Private company iSoon targets the US and Asia
In February 2024, leaked documents revealed that Shanghai-based company iSoon, under the guise of a cybersecurity training firm, conducted hacker-for-hire services for Chinese government agencies such as the Chinese Ministry of Public Security.
The group’s operations targeted U.S. and global entities, collecting sensitive data like GPS and audio recordings. iSoon also targeted the foreign ministries of Taiwan, India, South Korea, and Indonesia, according to the US Department of Justice.
The U.S. has since indicted Chinese hackers and offered a $10 million bounty for the espionage campaign. The US Treasury stated that the sanctions were necessary to protect US critical infrastructure and deter future attacks.
“State-sponsored hacking is an acute threat to our community and national security,” said Acting U.S. Attorney Matthew Podolsky for the Southern District of New York.
“For years, these 10 defendants — two of whom we allege are PRC officials — used sophisticated hacking techniques to target…government agencies…to gather sensitive information for the use of the PRC. These charges will help stop these state-sponsored hackers and protect our national security.”
H3: US Treasury Department hit with attack
In December 2024, Chinese state-sponsored hackers breached the U.S. Treasury Department by exploiting vulnerabilities in a third-party cybersecurity vendor, BeyondTrust.
A spokesperson for the Chinese Embassy in Washington rejected China’s responsibility for the hack, reinforcing that Beijing “firmly opposes the U.S.’s smear attacks against China without any factual basis.”
How devastating is this attack for the Treasury Department? Cybersecurity expert Ryan Kalember shares that Chinese hackers have frequently leveled supply chain attacks against the US government; however these attacks have not as yet caused irreparable damage.
On the topic of whether the hacking campaign originated from the PRC, Ryan Kalember states that it would be “no surprise whatsoever” if China claimed responsibility for the attacks.
What are the long-term geopolitical implications of Chinese-US cyber conflicts?
Heightened tensions, mistrust, and deepened geopolitical rivalries create a breeding ground to destabilize global norms and power.
In the long term, the Chinese government’s cyber espionage on rival nations could threaten US dominance on the global stage.
Here’s an overview of how US-China cyber conflicts could wreak havoc:
- Economic disruption: Cyber espionage from China could destabilize economies. Beijing is aggressively pursuing intelligence and intellectual property to become the dominant force in the 21st century.
- Fragmentation of global norms: Regional discrepancies between fundamental cybersecurity protocols create fragmentation. One example of this is China‘s restrictive firewalls.
- Less security online: The PRC directly opposes making the internet “secure and controllable” as Beijing presents “cyber sovereignty” as its core principle.
- Censorship and misinformation: Circulating false or misleading information and censoring information that goes against the PRC, such as censoring news organizations critical of China, creates a hostile business environment for overseas organizations.
How can organizations protect themselves against state-sponsored cyber threats?
Protecting your organization against state-sponsored threats is more important than ever.
Cybersecurity teams should remember to:
- Adopt a zero-trust model: Assume no user or device is trustworthy by default and enforce strict access controls and continuous monitoring.
- Perform regular updates: Ensure all software and systems are updated to address vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Train employees: Educate staff on recognizing phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics.
- Prepare an incident response plan: Develop and regularly test plans to respond effectively to cyber incidents.
Enhance your cybersecurity defenses
When countering state-sponsored threats, it‘s important to be proactive in your efforts. Threat intelligence and regular security assessments can provide robust protection against even the most sophisticated adversaries.
CybelAngel‘s External Threat Intelligence services help detect API risks and recover credentials stolen by malware.
