Threat Bulletin Stealers

Table of contents
Cyber threats are always evolving and it can be difficult to keep up with the latest developments. To help your company stay protected from external digital risks CybelAngel REACT (REsearch and Analysis of Cyber Threats) is releasing our threat bulletins to the public. We hope this information helps you, your company and customers safe.
I. Introduction
1. What is a stealer
A stealer (or infostealer / information stealer) is a type of malware, usually a Trojan. Its purpose is to collect information on the infected computer. Such information can be but are not limited to:
- Passwords saved in all browsers
- Cookies and history
- Credit Card information
- Global information about the computer (OS, Hardware, Installed Software…)
- Software credentials (Telegram, Discord, Steam…)
All the information collected by the stealer are then packaged into an archive, the archive itself is called a Log. With a log, in other words with a copy of a user’s most precious information, a malicious actor can easily take over the full control of the victim’s online identity. The passwords can indeed give access from dozens to hundreds of the victim’s accounts on any platform: email, gaming, online shopping, social network, entertainment, corporate, etc. In addition, the cookie values can be directly injected in a browser in order to connect on behalf of the victim, without even entering a password. While existing for a while, infostealers have recently gained in popularity (since 2019) with a real democratization of the malware across the different forums. We will take the RedLine stealer as an example when it is needed because it’s a very complete stealer and is one of the most popular at the time of writing.
2. Different families of stealers
According to our research team, the top 5 stealers in 2022 are the following, based on their popularity on the dark web:
- RedLine
- Vidar
- Taurus
- Raccoon
- Azorult
Here is a non-exhaustive list of features borrowed from RedLine that helps distinguish a simple non-professional stealer from a powerful and versatile malware:
- Browser saved information: password, credit card, auto-complete
- FileGrabber: search and exfiltrate sensitive files based on extensions or path
- Data from FTP/Steam/instant messaging clients (Telegram, Discord)
- Cryptocurrencies wallet stealer
- Clipper: replace copied crypto address by an attacker-controlled one in clipboard
- Anti-VM capabilities
II. Stealer Specificities
1. Distribution
Like most Trojans, distribution is done via traditional channels:
- Gaming crack
- Cracked Software
- Fake Password Cracker / account recovering software
- Ads for a cleaner software
- Phishing
2. Logs
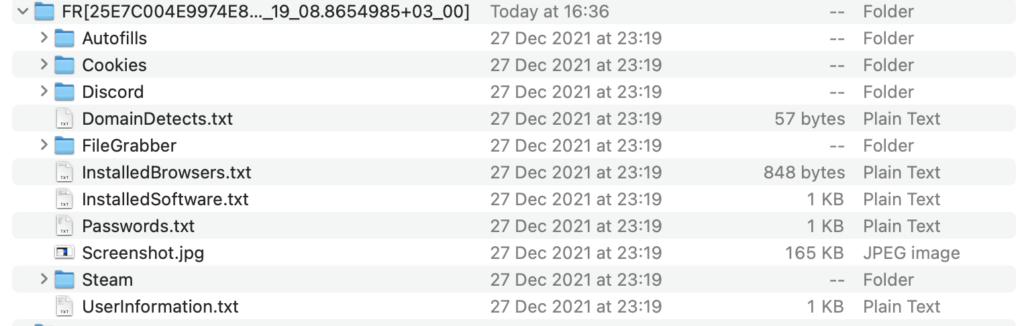
We can see the main information on the screenshot above, the name of the folder/archive is usually comprised of the country (FR), a unique identifier (25E7C004E9974E8D27E25DC7A828AB41), the date of infection with the time and the time zone (2021-12-28T01_19_08.8654985+03_00). The archive also usually contains a Screenshot.jpg which is a screenshot that the malware does just after infecting the computer. With this information we can sometimes guess the infection vector. 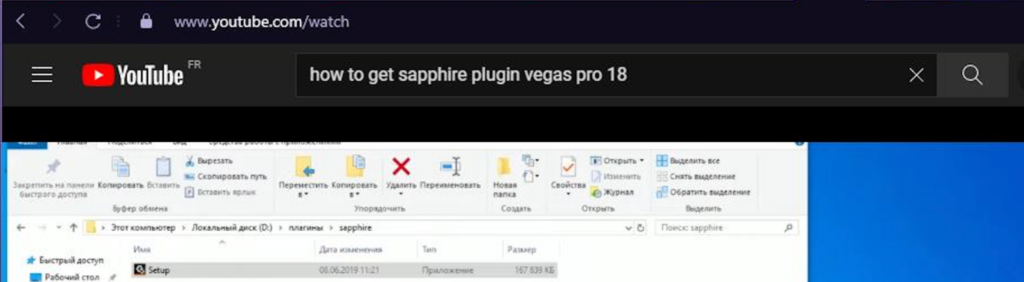
In this example, we can see that the user infected its computer by searching and downloading the cracked “Sapphire Plugin” for Vegas Pro 18 (a video editing software) on Youtube.
III. Economics
1. Stealer distributors
The Malware ecosystem has finished shifting to MaaS (Malware as a Service) and the infostealer industry is not an exception. The prices are roughly the same between the different strains of stealers. They usually range between $100 and 200$ a month and 1,000$ for a lifetime subscription. 
Redline Stealer Prices

Raccoon Stealer PricesL $75 for a 7 day trial, $200 for a monthly subscription
The main way of selling stealers is done via forums and instant messaging. Below is a non-exhaustive list for the RedLine Malware. Forums:
- Sinister.ly
- Wwh-club
- Skynetzone
- Opencard.us
- Dublikat.us.eu
- BHF
- Center-Club.us
- Dark2Web
- BTT-Club.top
- Blacknet.su
IM
- Telegram
2. Logs Marketplace
Most of the malicious actors infecting computers at scale with their stealers do not use the logs themselves, instead they sell it, via forums or via specialized sites like Russian Market or Genesis Market. The logs are usually sold around $10 on Russian Market and range from $1 to $150 on Genesis Market. Logs are a commodity for cybercriminals, and that’s one of the reasons they are so dangerous. With the information available on these underground markets, we can plot the market share of popular stealers and the map of infected countries: 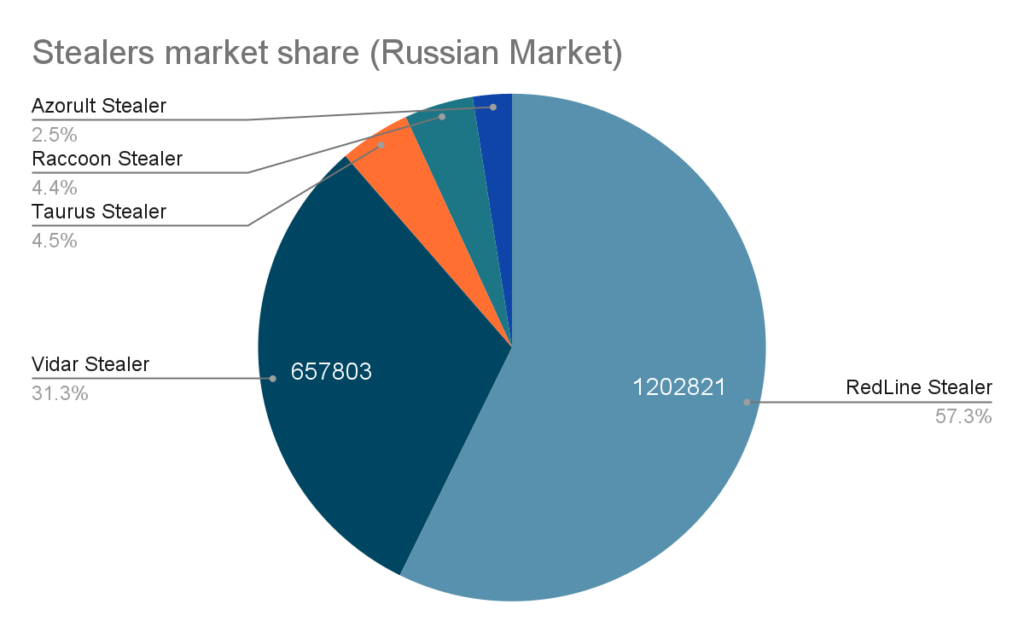
Stealers Market Share
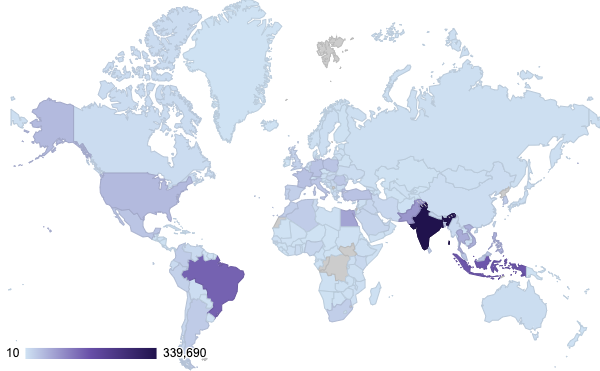
Infected countries
3. Why is it dangerous?
As we saw, the majority of the infected computers are personal computers because the distribution channels are usually related to leisure activities (gaming) or illegal ones (cracking accounts), though it is to be noted that certain actors focus specifically on infecting corporate devices, usually via phishing campaigns. Albeit, the ever-growing use of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), professional devices for personal activities and the reuse of passwords can quickly lead to business compromission. In fact, the Verizon 2019 Data Breach Incident Report, confirmed that 80% of hacking-related breaches still involve compromised and weak credentials. 29% of all breaches, regardless of attack type, involved the use of stolen credentials. During our research, we identified thousands of corporate accesses to internal applications, suppliers, corporate emails, VPN, RDP, FTP; especially on Russian Market and Genesis Market which are the most common platforms to trade logs.
