The Ultimate Data Protection Guide

Table of contents
According to CybelAngel, the amount of exposed data doubled last year.
Businesses are increasingly reliant on data to drive decision-making and operations. However, this also brings about heightened risks of data breaches and unauthorized access.
In this article, we’ll explore the difference between data privacy vs security, the importance of data protection for businesses, and strategies to safeguard sensitive information.
What is data privacy and security?
Data privacy refers to the protection of personal information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
On the other hand, data security involves implementing measures to prevent data breaches and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
There are some differences between data security vs privacy, but these two strategies work hand-in-hand. For example, encrypting sensitive customer data stored on a company’s servers demonstrates a commitment to data privacy and security.
Bonus terms
You may hear similar terms, such as data protection vs data privacy. Here’s a quick breakdown of the differences between them.
- Data privacy vs data protection: Data privacy refers to the proper handling, processing, storage, and usage of personal information to ensure it remains confidential, while data protection involves implementing measures and controls to safeguard data.
- Data security vs data protection: Data security focuses on safeguarding data from unauthorized access, cyber attacks, and other threats through technical measures, while data protection encompasses a broader range of practices, policies, and regulations.
The top 7 threats to enterprise data security
Data breaches and cyber attacks are daily news headlines, and businesses of all sizes are at risk.
Here are some of the top threats to enterprise data security:
- Phishing attacks: Commonly delivered via email, social media, or text messaging, where attackers trick employees into revealing sensitive information.
- Malware attacks: Malware such as infostealers, viruses, and ransomware can steal sensitive data or compromise entire systems.
- Insider threats: Employees can intentionally or unintentionally leak data or cause security incidents.
- Third-party breaches: Vendors, suppliers, and business partners can also be the source of data breaches in a supply chain attack.
- Unsecured endpoints: Mobile devices, laptops and other endpoints that connect to corporate networks, APIs, and apps can leave a business open to security vulnerabilities.
- Legacy technology: Outdated hardware or software systems can be vulnerable to attacks due to a lack of security updates or compatibility with modern security measures.
- Cloud security: Using cloud services can introduce security vulnerabilities. In fact, CybelAngel’s EASM report found that exposed data from cloud services has increased by 11%.
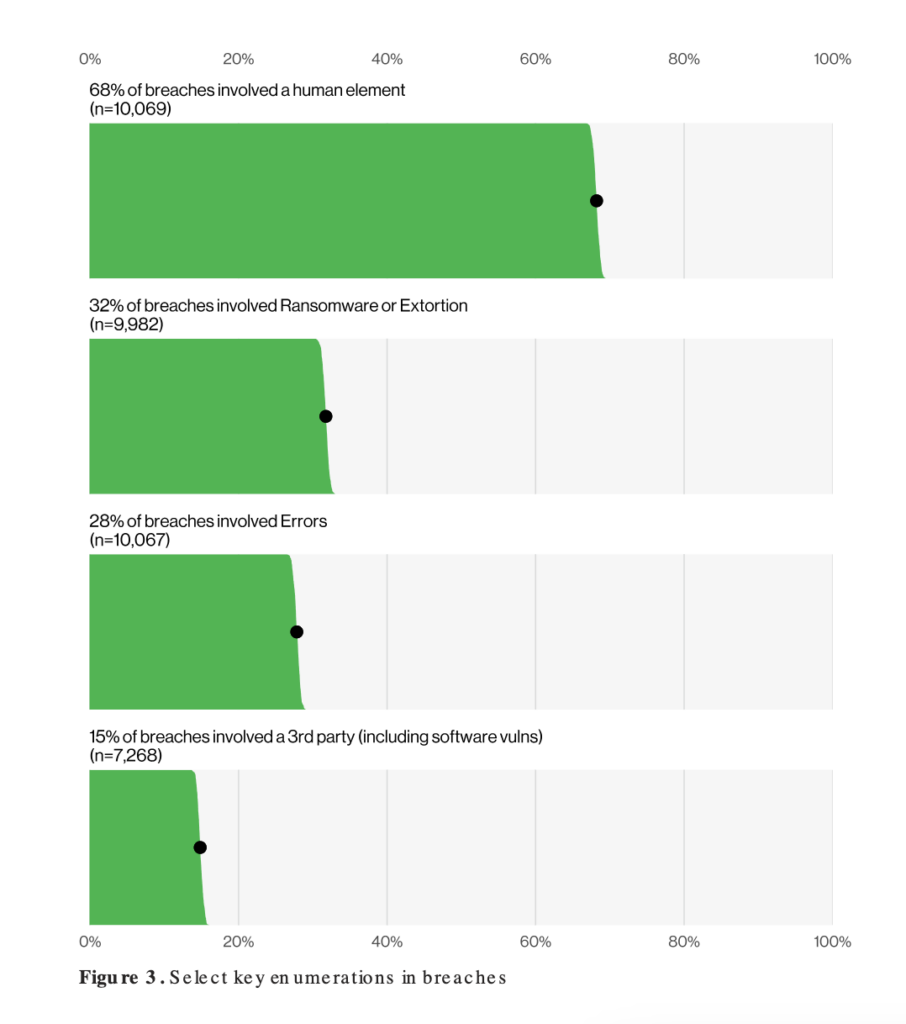
Ultimately, the biggest threat to information security is… People. A 2024 study by Verizon found that 68% of data breaches involved a human element.
Why is data privacy and security important?
The importance of data privacy cannot be understated. Here’s why data loss prevention should be your top priority.
- Legal compliance: Compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is crucial to avoid heavy penalties for data mishandling.
- Reputation management: A data breach can severely damage a company’s reputation and erode customer trust.
- Financial impact: Recovering from a data breach can be costly, including legal fees, compensation for affected parties, and system repairs.
- Risk mitigation: Implementing data loss prevention measures helps mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats, hackers, and unauthorized access.
- Protection of intellectual property: Safeguarding business data prevents the theft or deletion of intellectual property and proprietary information.
Plus, personal data is more vulnerable to cyberattacks than ever.
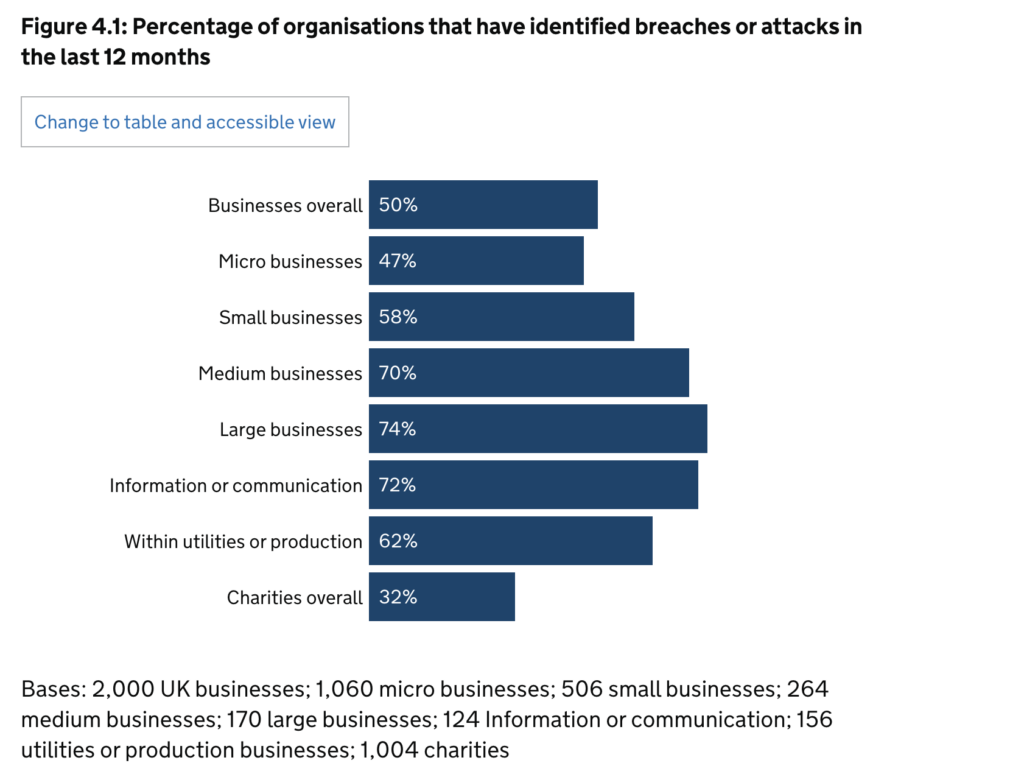
For example, a 2024 cybersecurity study by the UK government found that 50% of businesses had suffered a data breach or cyber attack within the last year.
How to protect your business data
There are plenty of cyber due diligence best practices that any company can adopt to keep data safe. From sticking to data governance guidelines to implementing API security tactics, here’s everything you need to know.
1. Don’t collect more user data than necessary
Good data management starts with sticking to the essentials. The more data you process, the more vulnerable you are to cybercriminals and identity theft.
Instead, limit the personally identifiable information (PII) you collect. Before you gather a piece of information, such as an email address, a social security number, or credit card details, ask yourself, “Do we really need this data?”
Also consider the lifecycle of your data—how long will you keep it until deletion is required?
2. Implement strong access controls
Implementing strict access controls, permissions, and multi-factor authentication is crucial for limiting access to sensitive information.
By requiring multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a unique code sent to a mobile device, companies can reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
3. Invest in EASM cyber security tools
EASM, or ‘external attack surface management’, is the process of protecting your public-facing assets from external threats, such as hackers.
EASM providers such as CybelAngel let you:
- Track and monitor your assets
- Prevent data breaches before they happen
- Avoid account takeovers
- Monitor the dark web for cybercriminal conversations
- Protect your domain
By understanding your digital footprint with alerting and data storage insights, you can proactively avoid data breaches and safeguard information privacy.
4. Prioritize API threat detection
50% of organizations have experienced data breaches due to API vulnerabilities, making this a top priority for any company.
For example, CybelAngel has just launched an API Threat Detection solution. This tool can spot any vulnerable external-facing APIs before they can be exploited.
It will:
- Deliver visibility: Spot unknown endpoints and identify any API threats
- Allow 24/7 discovery: Scan for any web application security issues in real-time
- Integrate with your systems: Enjoy easy setup and daily monitoring
You can read all about it in this comprehensive API Threat Detection ebook.
5. Focus on data encryption
Data encryption is a powerful tool for securing sensitive information both at rest and in transit.
By encrypting data, it is transformed into a coded form that can only be accessed with the appropriate decryption key. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable and protected.
6. Facilitate regular data backups
Only 6% of businesses without a data backup and recovery plan will survive long-term. Implementing regular data backups is essential for businesses to ensure quick recovery in the event of data loss.
Automated backups should be performed at regular intervals, ensuring that the most up-to-date information is securely stored. By having backups readily available, businesses can minimize downtime and restore critical data efficiently.
7. Offer employee training
Employee training plays a vital role in maintaining data security within an organization. By educating employees on cybersecurity, businesses can foster a culture of security awareness.
Training should cover topics such as identifying phishing attempts, creating strong passwords, and recognizing potential security threats.
Employees who are knowledgeable about data security are more likely to be vigilant and safeguard sensitive information, minimizing the risk of data breaches caused by human error or negligence.
8. Involve third parties, too
98% of organizations are connected with a third-party vendor that has suffered a data breach. You’re only as strong as your weakest link, which is why it’s vital to include vendors in your cybersecurity protocols, too.
Ask them to participate in your employee training programs, if possible, and to share clear documentation on how they manage their own data and network security systems.
9. Follow data protection laws and regulatory requirements
Stay ahead of the latest developments in data privacy regulations. These exist to protect the individual rights of your users and clients, and they have comprehensive guidelines on how to safeguard sensitive data.
Here are some quick examples, although laws may vary depending on your jurisdiction.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): A European Union law to safeguard people’s information privacy
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): A US healthcare law to protect patients’ health information
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): A US law to protect the privacy rights of California residents
10. And in the event of a data breach…
What should you do if sensitive data is compromised?
It’s crucial to:
- Contain and mitigate the data breach: Immediately isolate affected systems and devices to prevent further unauthorized access.
- Notify the relevant authorities: Comply with legal and privacy regulations by reporting the breach to the authorities and affected individuals.
- Review what happened: Audit the breach to determine the root cause, implement necessary remediation measures, and prevent future incidents.
The future of data privacy and security
In 2024, we can expect enhanced regulatory frameworks. Since GDPR was unveiled in 2018, stricter data privacy laws have become increasingly prevalent to address cyber threats and privacy concerns.
We can also anticipate an increased focus on data ethics. Businesses will prioritize ethical data practices, ensuring transparency and accountability in data collection and processing.
Conclusion
At the end of the day, protecting your business data isn’t just about compliance. It’s about protecting your reputation, and securing your operations for years to come.
With the right cybersecurity practices and data protection measures, you can proactively avoid data breaches and maintain the trust of your stakeholders and clients.
