The Cl0p Ransomware Gang Unveiled

Table of contents
Ransomware attacks aren’t just about locking up files anymore. The Cl0p ransomware group has taken extortion to a new level (a quadruple level, to be precise), shifting from encryption-based tactics to outright data theft. And they’re making millions doing it.
From exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities to targeting major corporations, Cl0p has cemented its reputation as one of the most sophisticated cybercrime syndicates in the world. In this deep dive, we’ll break down who Cl0p is, how they operate, and how to defend against them.
1. What is Cl0p ransomware?
Cl0p, “Clop” or TA505, is a notorious ransomware group that has gained global attention for its advanced cyber extortion tactics.
First observed in 2019 as a variant of the CryptoMix ransomware family, the Cl0p/ Clop ransomware gang quickly became a major threat.
According to The Hacker News, it’s believed to be a Russian gang, and the name seems to come from the Russian word “klop”, meaning bed bug.
Encrypted files have .clop extensions added. Like many other Russian-speaking threat groups, Cl0p cannot function on devices within the CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States).
However, unlike traditional ransomware groups that rely solely on encrypting files to demand ransom, Cl0p has evolved to use a combination of data theft and a quadruple extortion model.
This means victims who refuse to pay risk having their stolen data leaked publicly on their Tor-hosted data leak site, known as ‘CL0P^_-LEAKS’.

2. Cl0p ransomware in numbers
The ransomware market is growing, with a CybelAngel report detecting a 42% increase in reported attacks, plus a 125% increase in active groups in 2024.
Cl0p’s impact is substantial, both in terms of financial losses and the number of victims:
- More than $500 million in ransom payments have been extorted by Cl0p.
- Over 130 organizations were compromised in a single ransomware attack exploiting GoAnywhere MFT in early 2023.
- $75-100 million earned from the MOVEit transfer campaign alone in 2023.
- Cl0p ransomware emerged as the most active group in Q4 2024, overtaking RansomHub and Akira.

3. The Cl0p ransomware timeline
But where does Cl0p come from? How did it become one of the most notorious ransomware gangs in 2025?
Here’s a quick breakdown of its activities since 2019.
- February 2019: Cl0p is first observed in action, sometimes demanding payouts as high as $500 million.
- December 2019: Cl0p encrypts 267 Microsoft Windows systems at Maastricht University.
- December 2020: Hackers used zero-day vulnerabilities and a new web shell (malware to gain remote access). They managed to breach up to 100 companies, threatening to post the stolen data on Cl0p’s data leak site unless a ransom was paid.
- June 2021: Ukrainian authorities announced that they had arrested 6 suspected members of the Cl0p ransomware gang, working in collaboration with South Korea and the US (see video below).
- January 2023: Cl0p claimed responsibility for exploiting the GoAnywhere MFT file transfer appliance, breaching 130 organizations including major banking and healthcare organizations.
- Summer 2023: Cl0p used a zero-day vulnerability in the widely used MOVEit Transfer software to steal data from high-profile companies including British Airways, the BBC, and Boots.
- December 2024: The Cl0p threat group announced on its Tor-based website that it will name over 60 victims, after exploiting the software group Cleo.
- February 2025: The Cl0p group posted the details of 182 Cleo victims on its data leak site.

4. How a Cl0p ransomware attack works
Cl0p threat actors operate under a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, where affiliates distribute the malware, and the core operators manage ransom negotiations and infrastructure.
Cl0p cyberattacks primarily target large corporations, “surmising that they may be more willing and able to pay large ransoms since a disruption to their services or breach of their sensitive data is incredibly damaging,” according to a Tech Informed article.
Exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities
Cl0p has frequently also taken advantage of zero-day vulnerabilities.
These are unknown security flaws that criminals can exploit before anyone has a chance to stop them, hence the name “zero day”, since there are zero days of protection.
An example of this is the MOVEit transfer attack in 2023, where Cl0p found a hidden flaw in the file transfer software and used it to steal data from hundreds of organizations worldwide.
Because the vulnerability was unknown at the time, companies had no way to protect themselves until it was too late.
Embracing a quadruple extortion model
Cl0p’s tactics have evolved into what is now known as quadruple extortion. Initially, they may employ standard encryption-based extortion, followed by data theft and publication on leak sites to pressure victims.
If these methods fail, CL0P escalates further. Quadruple extortion adds two additional layers of coercion. Ultimately, it exploits both technical and psychological weaknesses.
One of these layers is Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, rendering websites and services inoperable until payment is made.
The second involves targeted harassment of stakeholders, including employees, customers, and even media outlets, to amplify reputational damage and internal pressure.
Moving away from encryption
In recent years, Cl0p has moved away from traditional encryption-based ransomware to “encryption-less” attacks.
Instead of locking files, they simply steal the data and threaten to leak it straight away, unless a ransom payment is made.
This shift allows them to bypass certain security measures and increase their ransom demands.
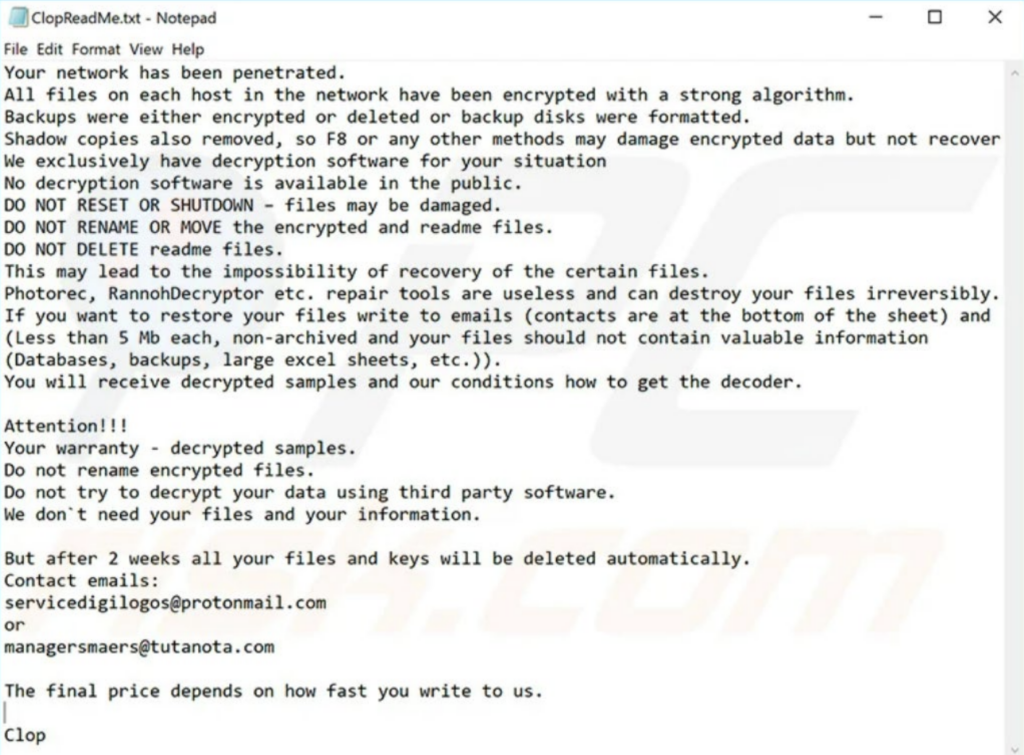
5. Case studies: Cl0p ransomware attacks
Here are some of the most infamous examples of Cl0p ransomware in action, with far-reaching consequences across the world.
The Accellion data breach (2020)
In December 2020, attackers infiltrated Accellion’s outdated File Transfer Appliance (FTA). In doing so, they gained access to sensitive files from nearly 100 organizations.
The breaches were attributed to the Cl0p ransomware gang and the FIN11 threat group. However, unlike their typical operations, the attackers did not deploy Cl0p’s file-encrypting malware.
Instead, they focused entirely on extortion. After the data exfiltration, they contacted victims via email, demanding payment to prevent the release of stolen information on the Cl0p data leak site.

The MoveIt transfer breach (2023)
In May 2023, CL0P exploited a newly discovered SQL injection vulnerability (CVE-2023-34362) in Progress Software’s MOVEit Transfer.
The attack was highlighted as a “global privacy disaster.” Thousands of firms suffered data breaches, with the estimated total cost of the incident reaching $12.15 billion.
In response, the FBI and CISA released a joint advisory detailing the tactics, indicators of compromise (IOCs), and mitigations linked to the CL0P ransomware group.

The Cleo breach (2024—present)
In December 2024, Cl0p took credit for a wave of cyberattacks targeting vulnerabilities in Cleo’s enterprise software. With Cleo serving over 4,200 organizations, the potential scale of the data breach is significant.
Cl0p initially targeted a flaw tracked as CVE-2024-50623, which enables unrestricted file uploads and downloads, potentially leading to remote code execution. Despite multiple security patches from Cleo, Cl0p continued to exploit other critical vulnerabilities.
In February 2025, Cl0p posted the details of 182 Cleo victims on its leak site according to security researchers on Twitter/ X (see below).
6. Defending against Cl0p ransomware
Given Cl0p’s sophisticated techniques, organizations must adopt a proactive cybersecurity approach to mitigate risks. Here’s how:
Patch and update systems regularly
Cl0p frequently exploits zero-day vulnerabilities in third-party applications. Regularly applying security patches, especially for software like MOVEit, GoAnywhere MFT, and Accellion FTA, is crucial—as is doing regular vulnerability assessments.
Implement strong email security measures
Cl0p’s phishing campaigns rely on deceptive emails. Organizations should:
- Deploy advanced email filtering solutions to block malicious attachments and links.
- Conduct regular security awareness training to help employees recognize phishing attempts.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect against stolen credentials.
Monitor for unusual network activity
Cl0p engages in extensive reconnaissance and lateral movement before executing attacks. Security teams should:
- Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to detect anomalies.
- Implement network segmentation to limit lateral movement.
- Continuously monitor logs for signs of compromise.
Secure data transfers and backups
Since Cl0p targets file transfer systems, companies should:
- Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
- Regularly back up critical files and store them in offline or immutable storage.
- Restrict access to file transfer tools to prevent unauthorized use.
Have an incident response plan
Preparation is the key to minimizing damage. Organizations should:
- Develop and test incident response playbooks.
- Conduct tabletop exercises simulating Cl0p ransomware scenarios.
- Have a clear policy on whether to negotiate with ransomware actors.
Invest in cyber intelligence
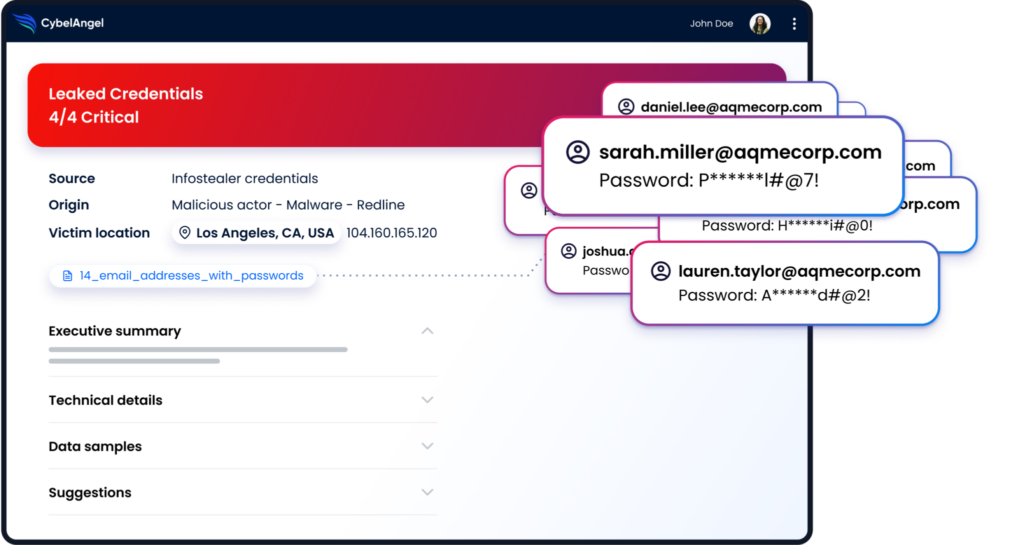
Tools like CybelAngel can help you to stay one step ahead of Cl0p ransomware groups, using a range of our solutions such as:
- Asset discovery and monitoring: Detect API threats and vulnerable assets before Cl0p ransomware can exploit them.
- Data breach prevention: Identify and secure potential data leaks before they escalate into major Cl0p ransomware incidents.
- Account takeover prevention: Prevent your stolen credentials from being sold on the dark web and used in phishing, ransomware, or other Cl0p extortion schemes.
- Dark web monitoring: Gain insights into cybercriminal activity from ransomware gangs like Cl0p by tracking discussions and threats on the dark web.
- Brand protection: Identify and eliminate malicious domains, fake social media accounts, and fraudulent apps posing as your brand.
- Remediation services: Minimize downtime by up to 85% in the aftermath of Cl0p ransomware attacks or other cyber threats.
Wrapping up
Cl0p ransomware is one of the most advanced cybercriminal operations today, continuously adapting to maximize profits.
By shifting from traditional encryption-based attacks to quadruple extortion, the group has increased its impact and financial gain.
Defending against Cl0p requires a multi-layered cybersecurity strategy, with support from advanced tools like CybelAngel to secure your network.
Book a demo call to learn more about how CybelAngel can secure your organization against threats such as Cl0p ransomware.
